In addition to imparting basic knowledge and developing individual competencies, today’s universities operate as a large community and social group. Facilitating the interaction between students, teachers and peers, stimulating their enthusiasm for active learning, will help students better integrate into social groups in the future. Therefore, in social interaction, social learning emerges as the times require and is more and more valued by schools. Therefore, how social learning should be carried out is extremely important. In order to respond to the requirements of social learning theory, combined with the new school of interconnected curriculum theory, business aesthetics, etc. It is required to break down the boundaries between schools and communities, and propose a new type of community activity to promote social learning activities – Learning fair, a social platform that connects schools and communities.
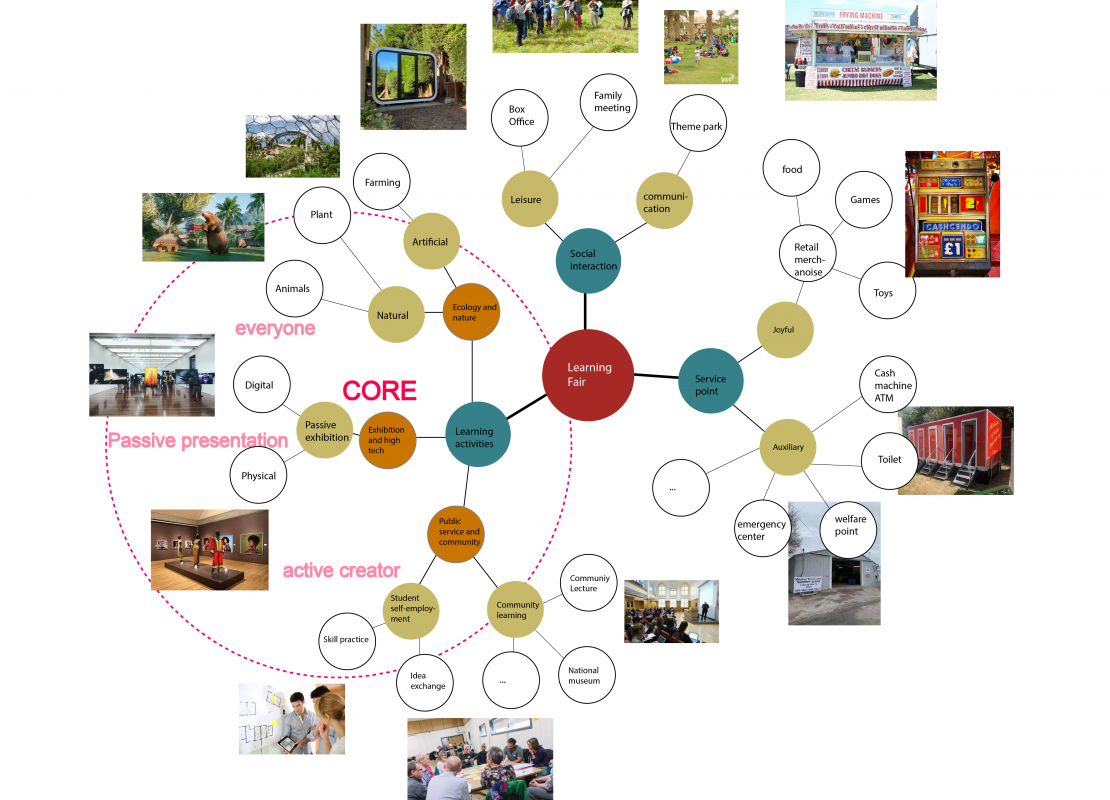
In order to better organize a complete learning fair, I studied the content of traditional fairs and classified the activities of learning fairs. These are learning activities, social interaction, and service functions. According to the previous analysis of users and learning styles, learning activities can be divided into three categories. The first is the Exhibition and high tech category for passive learning, where students or community organizations (such as national museums) can present their work to others physically or electronically, and the second is for co-crearing Public service and community, through seminars, lectures, and exchange meetings, to actively promote the interaction between students and social personnel, exchange of ideas, and students can further exercise the skills that students have acquired. As a garden, for a more general population, the integration of the nature museum can better enhance the function of the park itself.In addition to the learning function, social activities also play an important role in attracting the general population. Through the introduction of theme parks, family activities, etc., the audience of the learning fair will be expanded, which will help to shape the overall joyful feeling of the fair, and further transform the learning fair from the school to the society, so that everyone is exposed to the same kind. At the same time, for traditional fairs, in addition to entertainment facilities, service functions such as food and catering also play a crucial role in attracting crowds and enhancing crowd participation in fairs.
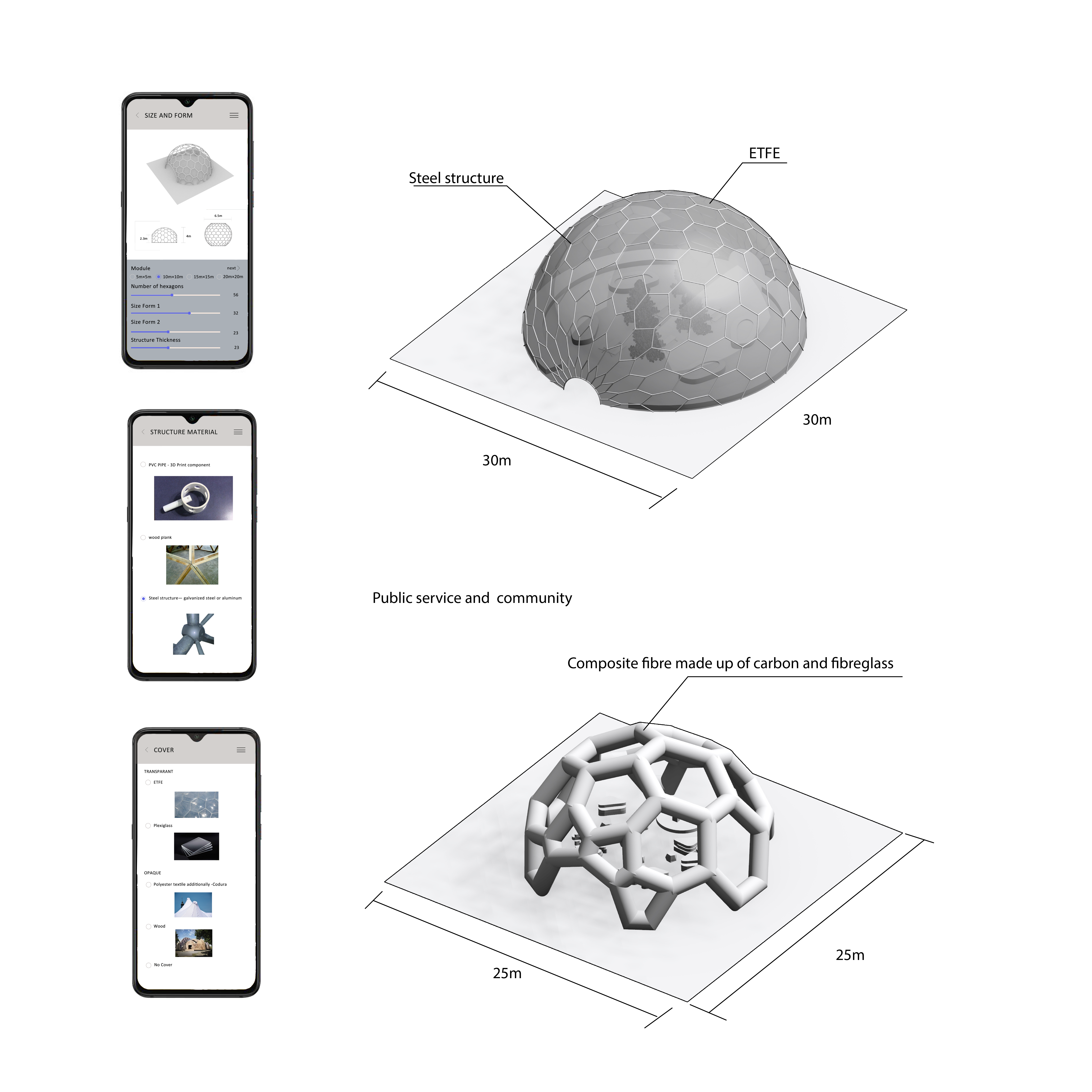
In my investigation, fair is temporary, flexible, and variable. The learning fair I want to create is also a system that can be replicated, used multiple times, and used in different locations. The question then is how to make learning fair a system rather than a design. Habraken divides the entire design system into 5 levels in his Uses of Levels. In his hypothesis, the user can be regarded as a responsible party as much as the professional. He points out that in the real world, hierarchies allow us to organize work in a more complex way. We no longer have to seek similar solutions for all purposes, but we can find the best approach in each situation. In each project, we can ask ourselves how to assign responsibility at different levels to get the best results in the most efficient way. Designers and users can design together, designers provide a framework, and users can adjust according to the framework, so as to achieve their various purposes. In different places, time users can adjust the learning fair according to this framework.